Wireless Technologies Vs Traditional Wired Technologies
Wireless technology has revolutionised the way we communicate within building systems making it possible to access sensory environmental information from virtually anywhere within a modern smart building.
As the technological world continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, building owners can’t afford to fall behind. The demand for devices that are quick and easy to deploy has become a critical competitive advantage in today’s business landscape. Gone are the days when wired ethernet and coaxial cables were the go-to options for internet connectivity in homes and businesses. With the advent of Wi-Fi and other wireless technologies, the game has changed. Wireless transmission mediums have emerged as highly competitive options, offering unparalleled convenience and flexibility.
Overview of traditional wired technology within the built environment:
- Reliability: Traditional wired technologies have been working for a long time and have proven to be reliable and stable.
- Security: Traditional technologies are considered more secure since they don’t rely on radio waves to transmit data, making them less vulnerable to interference.
- Maintenance: Traditional technologies do not require much maintenance, but when it is time to upgrade the cabling, it can be a costly and intrusive ordeal.
- Cost: Traditional technologies involve more costs and they are more expensive as they need qualified personnel to install the devices and provide the cabling from device to device.
- Fixed Infrastructure: Once the cables are run everything is fixed and if any changes are required it can be very costly to the owner or tenant of the building space.
Why is wireless technology the preferred communication method?
Wireless technology provides the ability to communicate between two or more devices over distances without wires or cables of any sort. This includes communications using radio frequency (RF) as well as infrared (IR) waves.
Wireless technologies provide a number of advantages for individuals and businesses such as:
- Mobility: Wireless technologies enable flexibility in mobility since they are not restricted by cables or wires, allowing users to collect and access information anywhere.
- Convenience: Wireless technologies do not require physical connections, making them easy to use, set up, and easy to relocate.
- Scalability: Wireless technologies are highly scalable, allowing them to be used in different settings, from homes and offices to large buildings and industrial environments.
- Cost: Wireless technologies can be less expensive as their installation does not require physical wiring and installation.
Past Wireless technologies and their challenges
While these technologies were innovative and convenient they also came with some problems that affected the communications performance, which negatively impacted users. Another major factor of past wireless technologies was the cost of the devices. In some cases, the wireless technology was more expensive than the wired solution.
Some wireless protocols which have had some challenges in the past are:
- Zigbee: A popular wireless communication protocol used in Internet of Things (IoT) devices. It is often used in home automation and industrial applications, such as building automation, lighting control, and sensor networks.EnOcean: An energy-harvesting wireless technology for building automation systems, such as lighting control, heating and cooling systems, and security systems.
- LoRa: LoRa (short for Long Range) is a wireless communication protocol designed for low-power, wide-area networks (LPWANs). LoRa is a proprietary technology developed by a company called Semtech, which is used by various companies and organisations around the world.
- Cellular: Cellular technology uses a combination of radio waves, digital signalling, and network infrastructure to transmit and receive data over the cellular network. The data is transmitted in small packets, which are received by the nearest cell tower and routed to their destination through a series of intermediate network nodes.
- BLE: BLE stands for Bluetooth Low Energy, which is a wireless communication protocol designed for low-power devices. BLE technology uses radio waves to transmit data over short distances (typically up to 100 meters) using very little power.
- Z-Wave: is a wireless communication protocol designed for home automation and smart devices. It is a technology used in smart homes for controlling and automating various devices, such as lights, thermostats, door locks, sensors, and more.
- Wifi: is a type of wireless communication technology that allows devices to connect and communicate with each other over a local area network (LAN) without the need for physical cables. It uses radio waves to transmit data between devices, such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, smart TVs, and other Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
The above technology and protocols for commercial building devices had different challenges in certain circumstances throughout their existence. Some of these are listed below:
- Security: Although Wireless technologies have built-in security features, they are still vulnerable to attacks such as replay and man-in-the-middle attacks, which can compromise the network’s privacy and security.
- Reliability: In large networks with many devices, certain protocols can become congested and slow down, resulting in delays or constant dropped connections. customers have complained constantly about how the devices lose connection and they stop working overall.
- Limited device selection: While different protocols have a growing number of devices available, they may not have as many options as other wireless protocols. It is important to understand what type of building services you are deploying and to make sure that the devices available meet the system requirements.
- Power consumption: While some devices use very low power, they still require a constant source of power. If the batteries run out, the device will stop functioning and may need to be replaced. Paying close attention to the battery life within the different technologies is a critical part of the design.
Cost: Some devices may be more expensive than other wireless protocols, which can make them less accessible for some users.
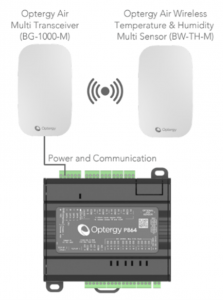
Wireless Sensors designed for change
The use of wireless sensors is gaining popularity due to their energy efficiency, scalability, and sustainability advantages. Unlike traditional wired sensors, wireless sensors require minimal equipment and installation infrastructure, reducing waste and promoting sustainability. With wireless sensors, you can optimise energy usage, reduce your building’s carbon footprint, and enjoy a host of benefits that make them an ideal choice for building owners.
Today’s Wireless sensors can detect and read a wide range of environmental metrics to provide users with all the information they need to understand and control their internal environment, and with the pleasing advantage of being battery-powered, wireless sensors can detect and read temperature, humidity & carbon dioxide. This is how wireless sensors provide enhanced data collection capabilities, allowing building managers to optimise energy usage and reduce the carbon footprint of their buildings.
Today’s wireless sensors are powered by long-lasting batteries that can operate for 5 to 10 years without maintenance, minimising the environmental impact associated with battery manufacturing, transportation, and disposal. Plus, with advanced wireless protocols and improved battery technology, wireless sensors offer reliability, functionality, and extended battery life, ensuring seamless performance for an extended period of time.
In addition to being energy efficient, wireless sensors are also aesthetically pleasing. They blend into or complement the environment they are deployed within, ensuring that your building’s aesthetics are not compromised. Installing wireless sensors is quick and simple, thanks to modern pairing methods and intuitive interfaces, saving you time and effort in deployment while achieving a seamless installation.
Industry experts state that one of the most significant sustainability advantages of wireless sensors is their ability to reduce the use of resources such as PVC conduit, galvanised steel conduit, copper wire, and plastic insulators. Unlike traditional wired sensors that require a vast wiring infrastructure, wireless sensors demand minimal equipment, resulting in a reduction of waste material during installation. This not only minimises the environmental impact of building projects but also reduces shipping costs and the carbon footprint associated with the transportation of materials, promoting a more sustainable future.
Benefits of today’s Wireless Sensors
- Sophisticated Design: Small, sleek sophisticated wireless sensors that maintain a modern professional design for contemporary spaces.
- Cost Reduction: Easy pairing and easy to install with one click, no need to run cables or re-wire if relocating.
- Versatility: Quick retrofits, moving to any desired location, and mounting on any surface without cables or wires.
- Extended Performance: Battery operated to support 5-10 years of accurate and reliable performance.
- Footprint reduction: Wireless sensors demand minimal equipment for installation, leading to a reduction in waste material that would otherwise end up in landfills. Furthermore, this minimal equipment requirement results in decreased transportation of materials, contributing to a reduction in carbon footprint.

Overall, wireless sensors are the smart choice for building owners who care about the environment. By choosing wireless sensors, you can significantly reduce your building’s environmental footprint while gaining access to accurate and up-to-date information about all the environmental metrics within your building environment. With wireless sensors, you can rely on real-time data to refine your building’s performance every day, promoting sustainability while ensuring optimal building management.